|
||
|
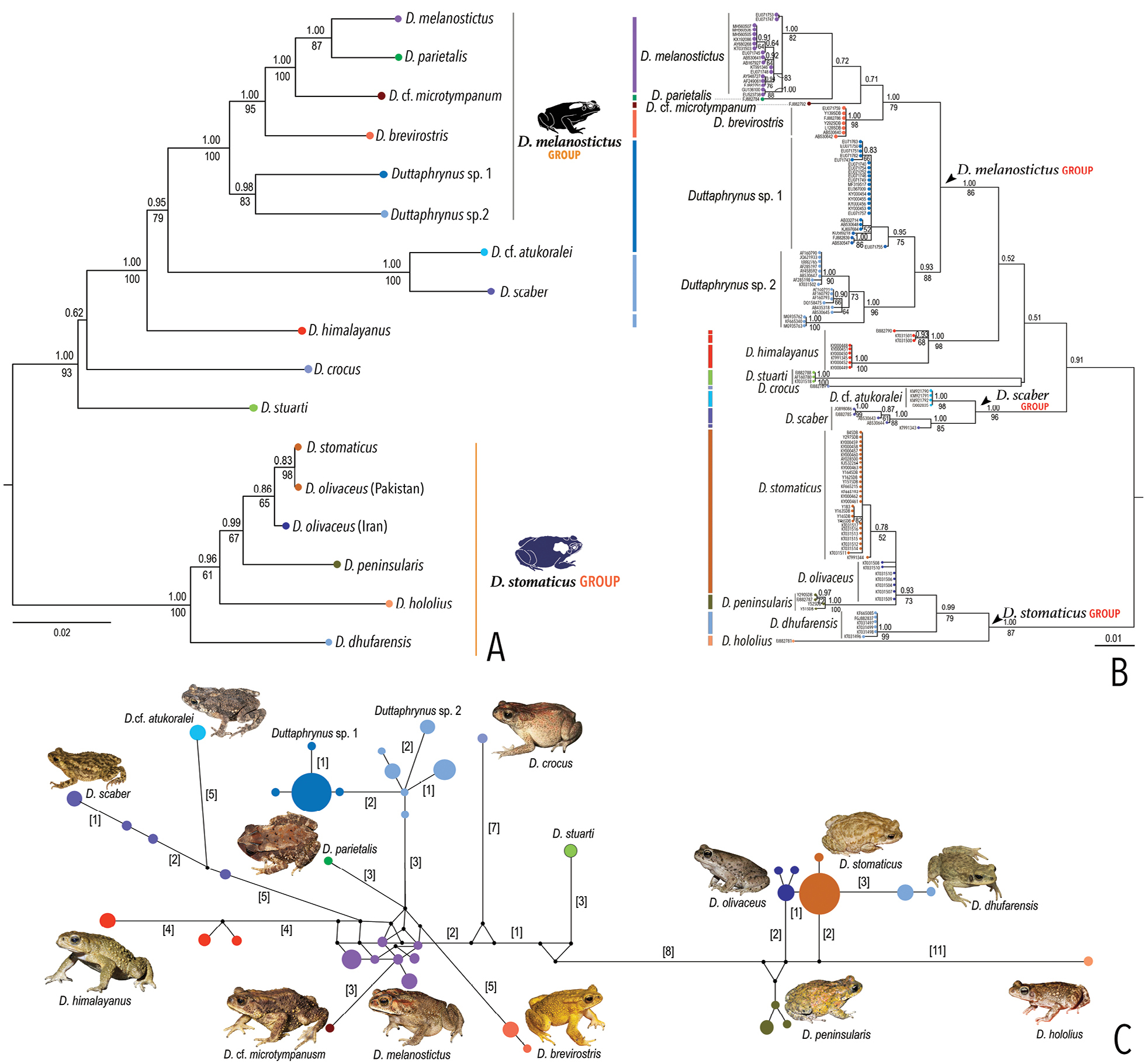
Phylogenetic relationships and genetic differentiation in the genus Duttaphrynus. A. Maximum Likelihood phylogenetic tree based on 5,737 bp DNA comprising nine mitochondrial gene regions and two nuclear genes, showing phylogenetic relationships between the major species-level lineages. Values above and below the branches indicate Bayesian Posterior Probabilities (BPP) and RAxML Bootstrap Support (BS), respectively; B. Maximum Likelihood barcoding tree based on 524 bp of the mitochondrial 16S rRNA sequences. BPP and BS support values are indicated above and below the branches, respectively. Coloured vertical bars outside the terminal node labels indicate putative species delimited in the bPTP analysis; C. Median-Joining haplotype network based on 42 haplotypes recovered from 133 sequences of the 16S gene (420 bp). Size of the coloured circles is proportional to the number of haplotypes; black circles indicate median vectors; each branch represents a single mutation step; additional mutational steps are indicated by values in parentheses; photo credits: D. crocus (Guinevere O. U. Wogan), D. olivaceus (Parham Beyhaghi), and D. dhufarensis (Todd W. Pierson). |