|
||
|
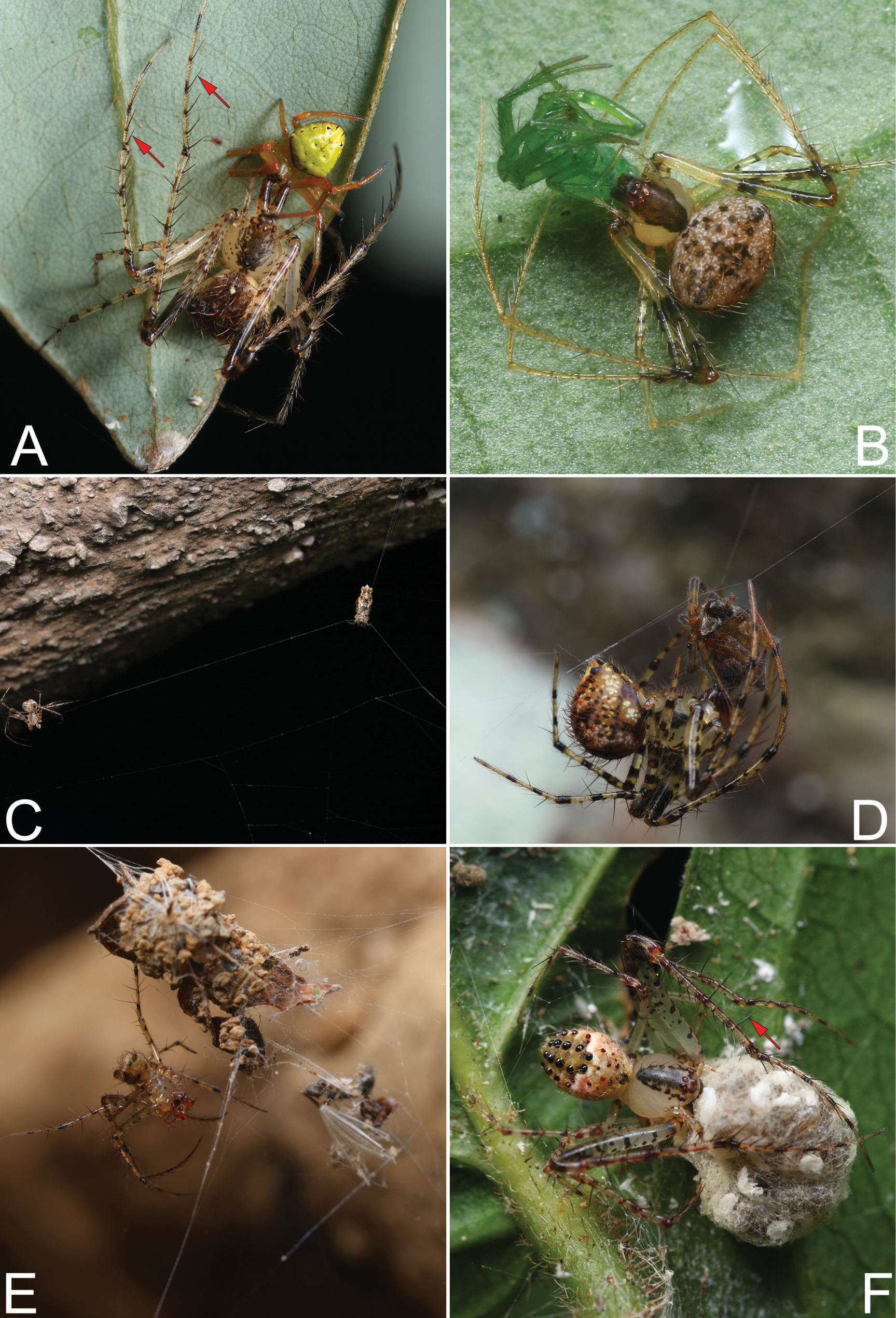
Araneophagic behaviors (A, B), predatory strategies (C–F), and rows of raptorial spines of mimetid spiders (A, F) A. Mimetus spp. has attacked and killed another spider of the family Araneidae; B. Mimetidae spp., feeding on an immature spider of an unknown family; C. Mimetidae spp. assaulting the web of a spider of genus Cyclosa; D. Mimetid at the end of a lunge toward and capture of a spider. Prey is held by a ‘basket’ formed by legs I–III of the mimetid. E. Mimetidae spp. had previously driven the resident from the web, thereby gaining exclusive access to the prey remaining on the web F. Mimetidae spp. wrapped up prey and scooped it up in a basket formed by legs I–III. Photographs by Q Lu (Shenzhen). Note: Red arrows in panel A and panel F point at raptorial spines on anterior legs. |